Digital targeting approaches are ways that digital advertisers can better target their audiences. Rather than marketing to anyone and everyone, this allows companies to target advertisements to a specific audience of individuals who are more likely to be interested and more likely to take action.
Start by defining your target market and what your buyer looks like in that market. Where do they spend their time? What websites do they visit? What products do they buy? What do they care about? Then use the appropriate targeting approaches to hone in on that target customer.
Here are six digital targeting approaches that every company should use in its digital marketing strategy.
1. Demographic Targeting
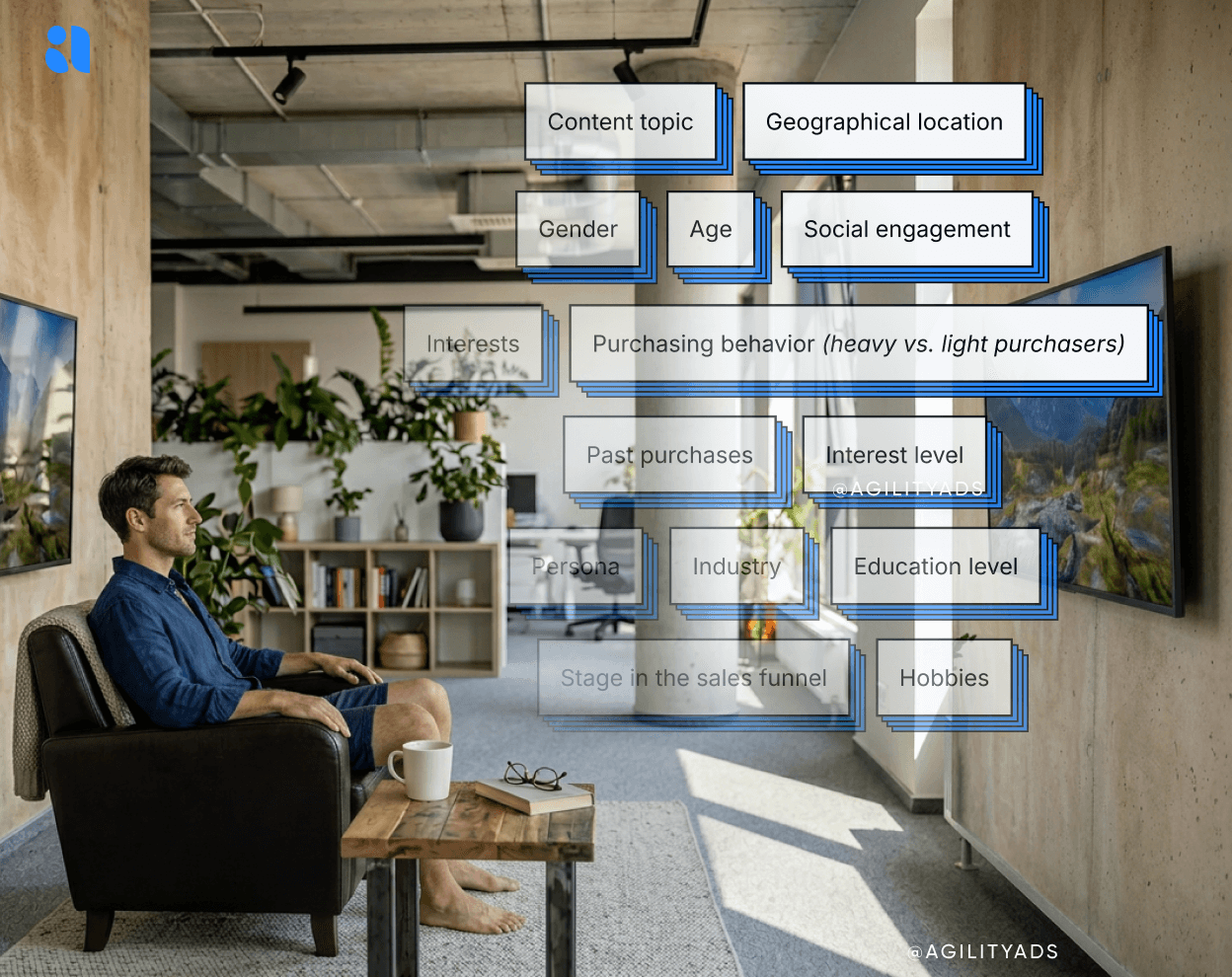
The most common form of digital targeting is demographic targeting. Using this approach allows companies to select specific traits of a consumer to target.
The exact demographics you can target depend entirely on the platform you advertise on. Some platforms offer more digital targeting approaches than others. Some of the demographic data that can be used when establishing an ad campaign include:
Gender
Age
Annual personal and/or household income
Occupation
Location
Nationality
Education level
Marital status
Number of children
Homeownership (own or rent)
Political affiliation
Religious affiliation
By using demographic information, companies are better able to place the right ad in front of the right person. For example, audience segmentation based on demographics helps a men’s clothing line target men instead of women, which helps them get the most from their marketing budget by not wasting precious advertising dollars on the wrong audience.
2. Location Targeting
Location targeting utilizes smartphone and GPS technology to actively identify where consumers are and deliver ads to anyone within a specific neighborhood or predetermined boundary.
This is different from utilizing the location demographic because location targeting focuses on much smaller geographic areas. It also considers if a consumer is actively there or has been there in the past, compared to the location demographic, which is more focused on which city or metropolitan area a consumer is from.
3. Similar Audiences
Similar audiences is a tool for businesses that have first-party data like a core list of customers or clients on their CRM and are looking to grow that list to include similar consumers who may also be interested.
This approach utilizes algorithms that monitor and track online behaviors. Everything—which websites people visit, the searches they run, and how long they spend online—is recorded. That information can be used to help businesses serve relevant ads to people who are similar to their existing customer base.
For example, a company that produces cooking tools and utensils might discover that its customer base searches for pasta and garlic bread recipes. By utilizing similar audiences, any time someone online searches for pasta and garlic bread recipes, they become a member of that similar audience and can be shown an ad for the company.
Additionally, social media platforms can provide valuable behavioral data, but advertising on platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and Instagram is a walled garden, meaning the targeting data, ads, and reporting stay on that platform. Advertising across the open internet, where people actually spend the majority of their time online, is a more effective way to reach the right group of people.
4. Affinity Audiences
Affinity audiences take the concept of similar audiences one step further. Rather than just showing a glancing interest in a topic, this targets an audience based on their habits and lifestyle. Affinity audiences have proven they have a focused passion for a certain topic, product, or action.
For the baking example above, instead of showing a casual interest in cooking with a single search, affinity audiences demonstrate repeated interest. This requires dozens of searches and consistent web traffic to cooking websites before they become a member of the affinity audience.
Affinity audience targeting helps businesses better reach out to customers who are experienced and interested in a particular topic. This allows the business to create custom, targeted ads that speak directly to the unique needs that only experts in a field understand or recognize.
5. Custom Affinity Audiences
Custom affinity audiences go another step further in qualifying an audience member before they are targeted with an ad. This differs from regular affinity audiences because it allows a business to establish its own affinity audience.
The company establishes the parameters of who they are targeting and can narrow it down by restricting it to people who have visited certain websites or even downloaded specific apps. While a narrow list of requirements can minimize the potential target audience, that can be beneficial in marketing because the advertisements become hyper-specialized.
The additional benefit to these custom audiences is that they can be used to target customers who are at different points in the funnel.
6. Retargeting Audiences
Retargeting is all about reaching out to people who have actually interacted with your brand. If a customer has visited your website or even made a purchase, retargeting allows you to target them.
Because they have already interacted with your brand or even made a purchase, there is a better return on investment in advertising to them because there is a higher chance for them to make additional purchases.
If you use Google Ads to retarget prospects, note that remarketing is the term they use in place of retargeting.
Choosing the Best Data For You
Obviously, the more targeted you are, the more you can tailor your messaging and creative, and the more confident you can be that you’re reaching the right audience. Provide them with relevant content, speak to their specific pain points, and design a call-to-action that they’ll actually want to follow. In turn, they see a better Return on Ad Spend (ROAS), boosts to other marketing metrics, and overall, more efficient marketing efforts across the board.
Be careful of being too broad with your filtered data. If you’re not sufficiently specific with your targeting you could end up wasting your ad spend on a different audience who have little to no interest in your product.
Amplify Your Digital Advertising with Agility
Using precision brand advertising, Agility targets your personas, produces high-quality ads, and serves them to your potential customers when and where they need them most. The results are higher conversion rates, boosted revenue, and better ROAS. Test precision brand advertising in your next marketing campaign to see the difference.
Share in...